Bowtie diagrams are entered via an intuitive graphical interface of the GRIF Risk module, a risk analysis software, which is easy to use. Initiating events can be entered quickly, and users can specify the frequency of occurrence, final events and their related level of criticality, as well as the barriers whose failure is defined according to the many laws available.
In the lower section, data can be input into a LOPA table. In this case, a scenario is created by entering the undesirable event (existing or new), the initial cause and the different barriers included in the protective measures. A bowtie model is created and automatically formatted in the data entry zone.
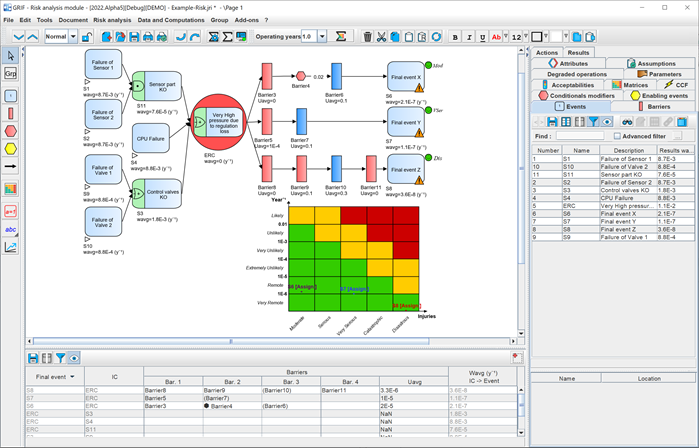
The ALBIZIA calculation engine developed by TotalEnergies produces a wide range of results:
- Instantaneous and average frequencies for all scenarios.
- Barrier demand frequency.
- PFD (Probability of Failure on Demand) and PFH (Probability of Failure per Hour) of barriers, which are specified in detail (periodic test, SIL loop, etc.).
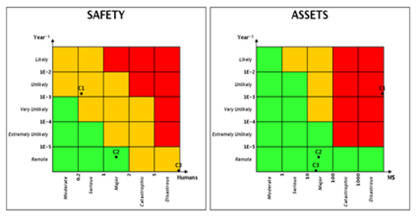
- Risk Reduction Factor required to remain within an acceptable risk zone.
- Importance factors (including Barlow-Proschan) to identify the barriers that need to be improved.
Bow-tie diagrams created in Risk can interact with any model of GRIF Boolean package: Fault Trees, Reliability Block Diagrams, SIS, etc. As a result, barriers or initiating events can be described in detail and the dependencies between barriers, which may have certain components in common, can be taken into account.
Once the Risk module has indicated the required Reduction Factor, a Safety Instrumented Loop can be added from the SIL module to the bowtie model via the Bool module. This approach ensures that the loop achieves the required PFD/PFH and confirms that the new frequency for each scenario is in an acceptable range.
In addition, the Safety Requirement Specification system helps users to comply with IEC-61508 or any other standards for which defining requirements is essential.